Risk of Cancer Increases with Age
Cancer risk increases exponentially with age, peaking in mean and women in their 80s. About 60% of cancers occur in people aged 65 and older.
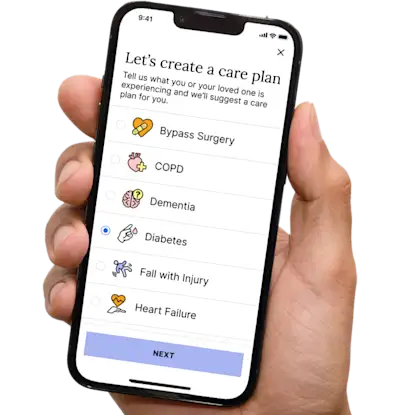
Get insurance benefits, legal documents, and medical records in one place

Helpful Highlights
The median age of cancer diagnosis is 66.
About 70% of the deaths caused by cancer are in those aged 65 and older.
There are more than 200 types and subtypes of cancer, and nearly half of all cancer cases are preventable.
Only 5-10% of all cancers are entirely hereditary, meaning 90-95% of cancers can happen with no family history of cancer.
There are more than 28 million cancer survivors worldwide.
In the elderly, cancer is one of the predominant causes of mortality and morbidity, and its incidence increases with aging. 60% of all cancer cases and 70% of cancer-related deaths occur in patients aged 65 years and over.
Why is cancer more prevalent in older adults and the elderly?
Scientists have known for years that age is a leading risk factor for the development of many types of cancer, but why aging increases cancer risk remains unclear.
Research and expert opinion suggest the prevailing reason is a prolonged build-up of cellular damage, called DNA methylation. The binding of chemical tags (called methyl groups) onto DNA affects interactions between DNA and the cell's ability to make proteins, making it easier to become a cancer cell. The longer we live, the more methylation we will have.
Other reasons are long-term exposure to carcinogenic (cancer-causing) agents, defects in genes that suppress tumor formation, broken cellular repair processes, oncogenic activation (normal cells undergo oncogene mutations that lead to the development of cancer), and lowered immunity.
The most common cancers in the elderly
(Note that these are not in any particular order.)
Colon cancer. More than 50% of colon cancer cases affect adults aged 67 and older. Thanks to prevention techniques, colon cancer is a less common diagnosis than other types of cancer and 63% of persons with colon cancer live 5 or more years after their diagnosis. Warning signs include changes in bowel habits such as more frequent diarrhea or constipation, bloody stool (which could be bright red or black), a feeling of fullness or a feeling of not being "done" after a bowel movement, persistent abdominal pain, aches or cramps, and unexpected weight loss.
Pancreatic cancer. Usually diagnosed in advanced stages, most cases affect adults aged 65 and older. Early warning signs include sudden-onset diabetes, jaundice (yellowing of the eyes and skin), itchy hands and feet, loss of appetite, loss of taste or smell, pale (clay-colored) or tarry (black, sticky) stool, and unexplained weight loss.

Bladder cancer. More than 70% of all bladder cancer cases affect men between the ages of 50 and 80, with more than 50% of cases occurring in those 65 and older. Warning signs are frequent urination, burning with urination, bladder spasms, bloody urine, distended bladder, and pelvic pain.
Prostate cancer. More than 50% of all prostate cancer cases affect men aged 75 and older. Although early warning signs are rare, some men experience symptoms prior to diagnosis. These include frequent urination, difficulty starting or stopping urine flow, burning sensation during urination, intermittent or weak urine stream, and bloody urine or ejaculate.
Prostate cancer is around 22 times more frequent among elderly men than among younger men.
Prostate cancer, along with lung cancer, are the most common causes of cancer death in men aged 85 and older, and together represent 40% of cancer deaths.
Breast cancer. The incidence of breast cancer among women aged 65 and older is almost two times higher than among women between ages 45 and 64, and ten times higher than women younger than 45. Early warning signs include a lump in the breast or armpit, swelling in the breast, changes in breast skin, or changes in the nipple (such as inverting or discharge).
Breast cancer is actually second to lung cancer as the leading cause of cancer death among women.
Lung cancer. More than 80% of all lung cancer cases affect adults age 60 and older, with more than 50% of cases occurring in those 70 and older. Warning signs include persistent coughing, chest pain, coughing up blood, difficulty breathing, and recurrent or chronic respiratory infections.
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer death in women, followed by breast cancer.
Lung cancer, along with prostate cancer, are the most common causes of cancer death in men aged 85 and older, and together represent 40% of cancer deaths.
Can cancer risk be reduced?
Yes! Even in older age. Probably not surprisingly, the ways to reduce cancer risk are the same as those promoted to reduce the risk of any other chronic illness or condition... Make healthy choices.
Stop smoking or never start
Maintain a healthy weight
Wear sunscreen (SPF of at least 30) and protective eyewear while in the sun
Limit alcohol intake
Eat a diet high in fiber
Reduce intake of processed foods, especially processed meats
Add more fresh fruits and vegetables
Get more active
If your loved one is over the age of 65 and has already been diagnosed with cancer, Cancer.net offers an excellent guide to navigating cancer care.
For more on cancer screenings, see our Guide Should Older Adults be Screened for Common Cancers?
RESOURCES
American Cancer Society, Facts & Figures 2021
American Cancer Society, Cancer in the Oldest Old
DeSantis, C.E., Miller, K.D., Dale, W., Mohile, S.G., Cohen, H.J., Leach, C.R., Goding Sauer, A., Jemal, A., & Siegel, R.L. (2019). Cancer statistics for adults aged 85 years and older, 2019. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians, 69(6), 452-467. DOI
Estape, T. (2018). Cancer in the elderly: Challenges and barriers. Asia Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing, 5(1), 40-42. DOI
No content in this app, regardless of date, should ever be used as a substitute for direct medical advice from your doctor or other qualified clinician.
Get more support and guidance on insurance benefits, medical records and legal forms.
Helpful brings together your insurance benefits, legal documents, and medical records in one personalized place — so you always know what you have, and never have to search again.
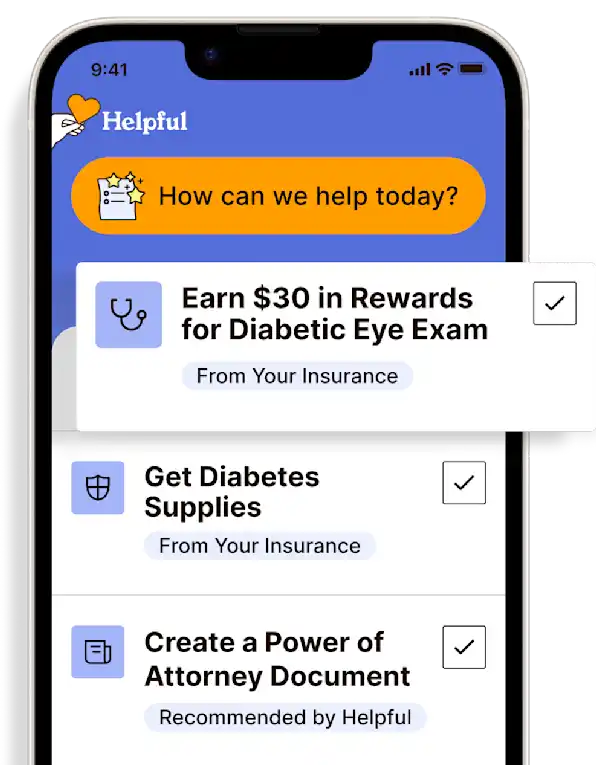
Technology for Health Tasks. Mental Health for the Tough Stuff.
Helpful connects your medical records, insurance, and caregiving tasks automatically. And when you need more than logistics, a therapist is here to guide you.
In-Network and Covered
For Individuals, Couples and Families
HIPAA Compliant, Data Stays Private