Pneumonia Risk Management and Prevention
Although older adults are at higher risk for pneumonia and complications, there are several easy means of prevention.
Get insurance benefits, legal documents, and medical records in one place

Helpful Highlights
Older adults (age 65 and older, especially 80 and older) are a high-risk group for pneumonia.
There are many, many simple ways to reduce risk and prevent pneumonia.
Regular hand washing and quitting smoking are the best first steps.
High-risk groups
Anyone can get pneumonia. However, the following groups are at the highest risk of contracting pneumonia or experiencing complications:
Adults ages 65 and older (especially 80 and older) and children younger than 5.
Especially older adults living in communal settings (large or multiple-family households, assisted living facilities)
People who have chronic medical conditions, like diabetes or heart or lung disease.
People with weakened immune systems (cancer, transplant, autoimmune).
Smokers.
Risk management and prevention
Lowering the risk
Annual flu shot
Pneumonia vaccination
Have a provider check any suspected complications with swallowing (aspiration can cause pneumonia)
Control existing medical conditions (especially heart or lung disease and diabetes)
Get testing for symptoms (influenza A & B, COVID-19)
Regular hand washing
Further lowering the risk
Eat healthy foods (a diet rich in fresh fruits and vegetables, high fiber)
Drink lots of fluids (clear liquids are best)
Limit alcohol intake*
Quit smoking
Get adequate rest (7-9 hours) at night
Stay active
Wash hands regularly
*National Institute on Alcohol and Alcoholism - people older than age 65, who are healthy and don't take medications, no more than seven drinks a week. American Diabetes Association - one drink or less a day for women, or two drinks or less a day for men.
Even more to lower the risk
Regularly clean and disinfect high-touch surfaces (door knobs, all handles, countertops).
Cough or sneeze into a tissue or the bend of the elbow.
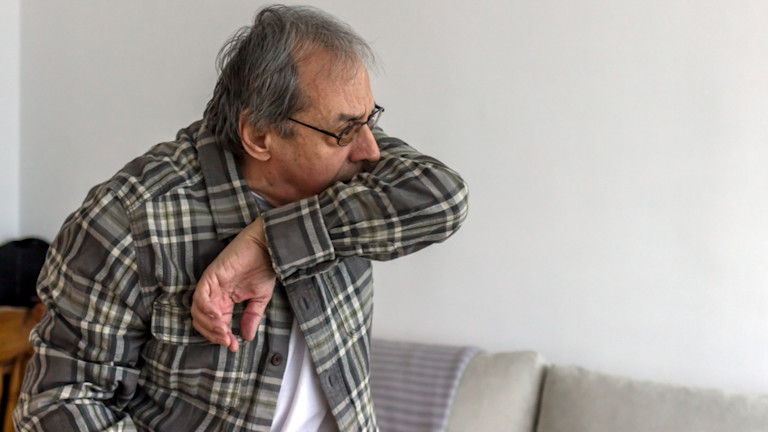

Quit smoking and avoid secondhand smoke. Smoking damages the lungs and makes infection more likely.
Stay away from others when sick.
Stay away from others who are sick (like grandchildren).
Avoid close contact and sharing items with others if either is sick.
RESOURCES
American Lung Association (ALA) - Pneumonia
American Thoracic Society (ATS) - Pneumonia
Johns Hopkins Medicine – Pneumonia
National Institute of Health (NIH) Heart, Lung, & Blood Institute – Pneumonia
World Health Organization (WHO) - Pneumonia
No content in this app, regardless of date, should ever be used as a substitute for direct medical advice from your doctor or other qualified clinician.
Get more support and guidance on insurance benefits, medical records and legal forms.
Helpful brings together your insurance benefits, legal documents, and medical records in one personalized place — so you always know what you have, and never have to search again.
Technology for Health Tasks. Mental Health for the Tough Stuff.
Helpful connects your medical records, insurance, and caregiving tasks automatically. And when you need more than logistics, a therapist is here to guide you.
In-Network and Covered
For Individuals, Couples and Families
HIPAA Compliant, Data Stays Private

Healthcare Tasks Simplified

From syncing records to spotting drug interactions, Helpful does the heavy lifting, turning complex health info into clear tasks and showing you benefits you can actually use, giving you clarity and control over your care.

In-Network Mental Health

Our licensed therapists are here to support you and your loved ones through stress, burnout, and life’s hardest moments, with an inclusive, compassionate approach that works with most insurance plans.

Create Legal Documents

Plan ahead by creating will, trusts, advance directives and more, that ensure your wishes are honored in the event you can’t speak for yourself -with Helpful guiding you every step of the way.