Malnutrition, a Public Health Issue for Older Adults
Malnutrition and undernutrition are concerns among older adults, particularly those living alone or with limited access to nutritious food.
Get insurance benefits, legal documents, and medical records in one place

Helpful Highlights
Malnutrition is a significant public health issue for older adults due to several reasons.
Given these factors, addressing malnutrition among older adults is essential for promoting healthy aging, maintaining independence, preventing adverse health outcomes, and reducing healthcare costs.
Public health efforts aimed at identifying and addressing risk factors for malnutrition, promoting access to nutritious food, providing nutrition education and counseling, and integrating nutrition screening and assessment into healthcare settings are critical for improving the nutritional status and well-being of older adults.
Increased vulnerability
Older adults are more vulnerable to malnutrition due to physiological changes associated with aging, such as decreased appetite, changes in taste and smell, dental problems, reduced gastrointestinal function, and impaired absorption of nutrients. These factors can lead to inadequate intake of essential nutrients, putting your loved one at risk of malnutrition.
Chronic health conditions
Many older adults have chronic health conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, cancer, and gastrointestinal disorders that can affect their nutritional status. These conditions may increase nutrient requirements, alter nutrient metabolism, or interfere with the ability to eat and digest food, further exacerbating the risk of malnutrition.
Polypharmacy
Your loved one may take multiple medications to manage their health conditions, which can have side effects such as appetite suppression, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and impaired nutrient absorption. Polypharmacy can contribute to nutritional deficiencies and increase the risk of malnutrition.
Social and economic factors
Social and economic factors such as limited income, social isolation, living alone, lack of transportation, and inadequate access to nutritious food can contribute to malnutrition. These factors may prevent your loved one from obtaining and preparing healthy meals, leading to poor dietary intake and malnutrition.
Functional decline
Functional decline associated with aging, such as loss of mobility, fine motor skills, and cognitive impairment, can affect your loved one's ability to shop for groceries, prepare meals, and feed themselves. Functional limitations can lead to dependence on you for food assistance and increase the risk of malnutrition.
Adverse health outcomes
Malnutrition among older adults is associated with adverse health outcomes such as weakened immune function, impaired wound healing, muscle wasting, and increased risk of infections, falls, hospitalizations, and mortality (death). Malnourished older adults are also more susceptible to complications from chronic diseases and have longer hospital stays and higher healthcare costs.
No content in this app, regardless of date, should ever be used as a substitute for direct medical advice from your doctor or other qualified clinician.
Get more support and guidance on insurance benefits, medical records and legal forms.
Helpful brings together your insurance benefits, legal documents, and medical records in one personalized place — so you always know what you have, and never have to search again.
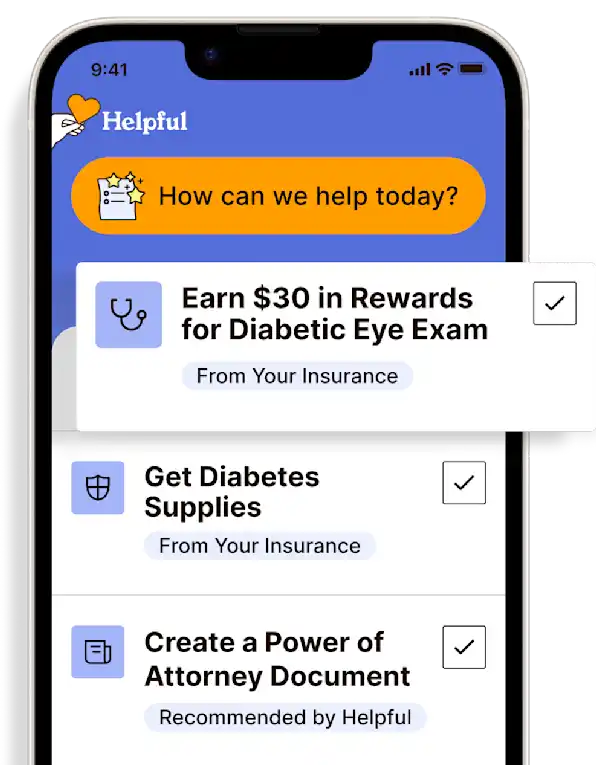
Technology for Health Tasks. Mental Health for the Tough Stuff.
Helpful connects your medical records, insurance, and caregiving tasks automatically. And when you need more than logistics, a therapist is here to guide you.
In-Network and Covered
For Individuals, Couples and Families
HIPAA Compliant, Data Stays Private

Healthcare Tasks Simplified

From syncing records to spotting drug interactions, Helpful does the heavy lifting, turning complex health info into clear tasks and showing you benefits you can actually use, giving you clarity and control over your care.

In-Network Mental Health

Our licensed therapists are here to support you and your loved ones through stress, burnout, and life’s hardest moments, with an inclusive, compassionate approach that works with most insurance plans.

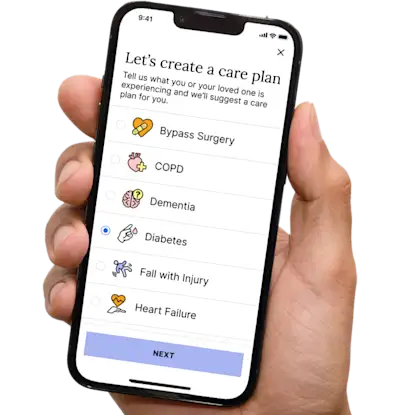
Create Legal Documents

Plan ahead by creating will, trusts, advance directives and more, that ensure your wishes are honored in the event you can’t speak for yourself -with Helpful guiding you every step of the way.