Stents vs. CABG for Heart Attack
There are two ways to clear blocked arteries that cause heart attacks - cardiac stent or coronary artery bypass graft (CABG).
Get insurance benefits, legal documents, and medical records in one place
Helpful Highlights
A cardiac stent is a metal cage placed in the blocked coronary artery to open it and restore blood flow. A stent cannot be used in all cases.
A coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) is a procedure wherein the blocked coronary arteries are clipped and rerouted ("bypassed") using vessels taken from elsewhere in the body.
Stents are often used to prevent a major heart attack by opening partially blocked coronary arteries (at least 70% blockage, with special exceptions for less).
As a caregiver, you can support your loved one by learning as much as possible about the coronary vessels that are blocked and what was - or is going to be - done about it. Help them, as well as yourself, by going with your loved one to all provider appointments. Many times, the information is so overwhelming that they will not remember some key points discussed and will hesitate to ask questions. With both of you listening, you’ll be able to prompt them to ask questions during the visit, as well as help them remember what the provider said. With greater knowledge about the condition, the procedure, and the recommendations, you will be able to provide total support for your loved one.
Stent vs. coronary artery bypass graft (CABG or "bypass")
Which is best? It’s not a toss-up, but the right choice depends on several factors, and this question actually has a (general) answer – bypass (CABG) – provided your loved one's surgery risk isn’t too high.
Why?
The question of stent versus bypass (CABG) is really for those who have multi-vessel disease involving the three main coronary arteries.* For three-vessel coronary disease, a bypass is superior to stents, with the possible exception of cases where the blocked part of the artery is very short.
The same is true when more than three vessels are involved; hence, "quadruple" bypass (four vessels), "quintuple" bypass (five vessels), and beyond.
In some cases, a combination of stent placement and bypass (CABG) surgery is done, which may be performed together - called hybrid coronary revascularization - or as separate procedures.
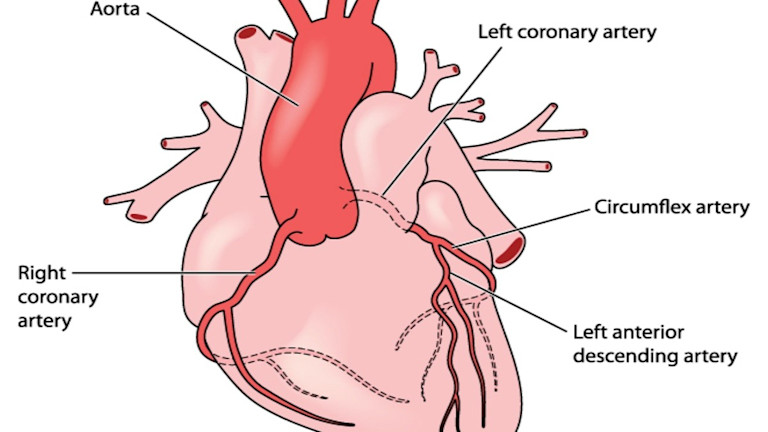
*The three main coronary arteries are taken to mean the left anterior descending (LAD) and the circumflex (Cx, also on the left) arteries - both of which branch from the left main coronary artery (LMCA) - and right coronary artery (RCA).
When stents are best
When the left anterior descending (LAD) artery isn't involved, or at least when it isn't mostly or completely blocked.
When there is a blockage in just one, maybe two vessels (but not the LAD). In this case, the cardiologist is likely to talk with your loved one about medical therapy versus stent placement. Medical therapy is medication, lifestyle changes, and follow-up visits without invasive interventions.
When a bypass is no longer an option due to health status or surgery risk.
Bypass (CABG) is best for the most important artery - LAD
The three main coronary arteries are not all equal. The most important of them is the left anterior descending (LAD) artery. It supplies blood to the entire front wall of the heart, which represents much more muscle than the area fed by either of the other two arteries. It also represents the left ventricle - the heart's main pump that supplies blood to the brain and body. A narrowing or blockage in the LAD is, therefore, the most serious.
Bypass (CABG) is the best choice for a mostly or completely blocked LAD. If the LAD is narrowed, and there are no other complicating factors, a stent might be used.
A stent in the LAD only protects the area of the blockage, however. The rest of the artery is still vulnerable. A bypass (CABG) protects the downstream portion of that vessel, as well, usually for life.
RESOURCES
American Heart Association (AHA) - Heart Surgery & Recovery Resources
Harvard Health - Bypass or Angioplasty with Stenting?
No content in this app, regardless of date, should ever be used as a substitute for direct medical advice from your doctor or other qualified clinician.
Get more support and guidance on insurance benefits, medical records and legal forms.
Helpful brings together your insurance benefits, legal documents, and medical records in one personalized place — so you always know what you have, and never have to search again.
Technology for Health Tasks. Mental Health for the Tough Stuff.
Helpful connects your medical records, insurance, and caregiving tasks automatically. And when you need more than logistics, a therapist is here to guide you.
In-Network and Covered
For Individuals, Couples and Families
HIPAA Compliant, Data Stays Private

Healthcare Tasks Simplified

From syncing records to spotting drug interactions, Helpful does the heavy lifting, turning complex health info into clear tasks and showing you benefits you can actually use, giving you clarity and control over your care.

In-Network Mental Health

Our licensed therapists are here to support you and your loved ones through stress, burnout, and life’s hardest moments, with an inclusive, compassionate approach that works with most insurance plans.

Create Legal Documents

Plan ahead by creating will, trusts, advance directives and more, that ensure your wishes are honored in the event you can’t speak for yourself -with Helpful guiding you every step of the way.