Pre-Op Prep for Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG)
Before bypass surgery, your loved one will need to make activity, diet, and medication changes, which includes items specific to surgery.
Get insurance benefits, legal documents, and medical records in one place
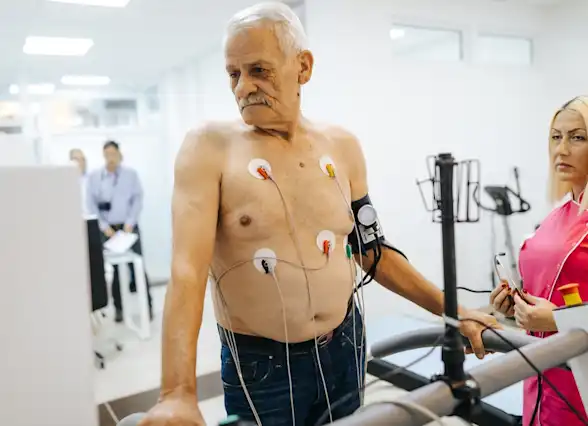
Helpful Highlights
The first and most important thing for your loved one to do is stop smoking (all tobacco use).
Medication and lifestyle management, and possibly other medical procedures, are implemented before bypass surgery and can sometimes prevent it.
There are many tests performed before surgery to determine if your loved one is safe and physically suitable to have it.
# 1 is smoking cessation
Smoking makes the heart work harder and puts coronary arteries at further risk of damage. Smoking also increases the risk of developing pneumonia or other pulmonary complications after surgery.
Pre-op prep
The cardiologist will provide individualized instructions on any lifestyle changes that need to be made, as well as activities that need to be added to your loved one's daily routine before surgery.
Medication and lifestyle management, and possibly other medical procedures (such as angioplasty*), are typically implemented before CABG. Sometimes these efforts even prevent bypass surgery. Your loved one will start medications that lower cholesterol levels and blood pressure, and improve blood flow through the coronary arteries if they aren't on them already. They will need to adhere to a heart-healthy diet and exercise recommendations, including those aimed at preventing complications following surgery.
*Angioplasty, also called balloon angioplasty, is a minimally invasive procedure wherein a balloon-tipped catheter is threaded into the blocked coronary arteries and inflated. Inflation pushes against the blockage and opens the artery, allowing increased blood flow. (The same procedure is used for stent placement.)
When deciding if your loved one is a candidate for CABG, the cardiologist will also consider the following:
Thorough physical exam
Health history and any past treatment of heart disease or other cardiac issues, including surgeries, procedures, and medications
History of other diseases and conditions
Age and general health and well-being
Family history of coronary artery disease, heart attack, or other cardiac conditions
Testing
Several tests (see below) will be performed to confirm that it's safe for your loved one to have bypass surgery. Likewise, blood and imaging will be collected to find out which arteries are clogged, how much they're clogged, with what, and whether there's any heart damage.
The potential tests include, but are not limited to:
Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG)
Echocardiogram
Exercise stress test
Nuclear cardiac stress test
Cardiac catheterization (angiogram)
X-ray angiography or computed tomography (CT) scan angiography
Coronary calcium scan
Complete blood count (CBC), chemistry (CHEM-12, 14), and lipid panel that analyzes cholesterol, blood sugar, electrolytes, and multiple other factors
Possibly urine tests that analyze kidney function
RESOURCES
American Heart Association (AHA) - Heart Surgery & Recovery Resources
Cleveland Clinic – Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery
Johns Hopkins Medicine – Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Surgery
Mayo Clinic – Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery
No content in this app, regardless of date, should ever be used as a substitute for direct medical advice from your doctor or other qualified clinician.
Get more support and guidance on insurance benefits, medical records and legal forms.
Helpful brings together your insurance benefits, legal documents, and medical records in one personalized place — so you always know what you have, and never have to search again.
Technology for Health Tasks. Mental Health for the Tough Stuff.
Helpful connects your medical records, insurance, and caregiving tasks automatically. And when you need more than logistics, a therapist is here to guide you.
In-Network and Covered
For Individuals, Couples and Families
HIPAA Compliant, Data Stays Private

Healthcare Tasks Simplified

From syncing records to spotting drug interactions, Helpful does the heavy lifting, turning complex health info into clear tasks and showing you benefits you can actually use, giving you clarity and control over your care.

In-Network Mental Health

Our licensed therapists are here to support you and your loved ones through stress, burnout, and life’s hardest moments, with an inclusive, compassionate approach that works with most insurance plans.

Create Legal Documents

Plan ahead by creating will, trusts, advance directives and more, that ensure your wishes are honored in the event you can’t speak for yourself -with Helpful guiding you every step of the way.