How to Create a Will or a Trust Document
In many states, a self-drafted will or trust is just as legal as one drafted by a lawyer, though having a lawyer create one may be a better option.
Get insurance benefits, legal documents, and medical records in one place

Helpful Highlights
Self-drafted wills and trusts can be legally valid in all 50 states and U.S. territories, but their validity and effectiveness can vary depending on several factors. The laws governing wills and trusts and the requirements for their validity can differ from state to state.
Though it may not be necessary, having a lawyer draft (or at least review) a will or trust ensures that all necessary elements are considered and covered.
For links to available wills and trusts templates by state, locate that state in our Legal Forms Stack or use our Search bar.
How to create a will or trust
Your loved one can either use online sources to download or buy will and trust templates, or have them drafted by a lawyer.
Your loved one needs to determine which type of will or trust is required, either by searching online or discussing with a lawyer or other estate planning professional.
The most frequently searched and readily available types of wills and trusts are Last Will and Testament (Last Will or Will) and Simple Trust (Revocable Trust or Trust).
Note that while a will can be relatively straightforward and thereby easier to self-draft, a trust involves several steps beyond just the document creation, which can become complex and create more room for error.
Errors or missing elements can invalidate a trust or a will.
SELF-DRAFTED
If a template is downloaded or purchased, make sure it contains everything required by that state. Will and trust documents are very important, and your loved one should not assume that downloaded or purchased documents are correct in meeting all state requirements.
Procedures and laws vary based on your loved one's residence. In many states, however, as long as your loved one follows the state's requirements, any will or trust they create is legally valid.
For a will or a trust, it is often mandatory to get your loved one's signature notarized. In most cases, witness signatures must also be notarized. In addition, some legal provisos are not applicable across all states.
Note that some states still consider handwritten wills or trusts legally valid. These are termed "holographic". If this is an option in your loved one's state, understand that the documents must still meet all state requirements (including authenticity and legibility) to be considered legally valid.
LAWYER-DRAFTED
If your loved one wishes to start the will or trust process with a lawyer, they will need to locate an estate planning, family law, or elder care attorney in their state of residence (preferably in their local area) and request a consultation.
If the associated legal fees are more than your loved one can manage, there is the option of visiting a legal aid office. Alternatively, your loved one can go to the Legal Services Corporation website and communicate with a legal aide. Consultations are free for those who are eligible.
The most common self-drafting mistakes
WILLS
Missing or improper signatures
Failing to name an executor, or naming an unsuitable executor
Including assets your loved one doesn't own or that already have a designated beneficiary
Not understanding the tax implications for the beneficiaries or protecting them from creditors
Failing to review and revise the will according to changes in situation
Failing to remove standard template language that doesn't apply
TRUSTS
Having an improperly drafted trust document - many experts will say the biggest mistake is drafting it yourself
Failing to designate successor trustee(s), or naming co-trustees rather than successive backup trustees
Restricting trustees too much
Not restricting beneficiaries enough, or not building in adequate beneficiary contingencies
Not funding the trust, or improper transfer of assets to the trust
Believing a trust is all that's needed for future/estate planning
Failing to review the trust regularly (if revocable)
RESOURCES
National Council on Aging (NCOA)
No content in this app, regardless of date, should ever be used as a substitute for any direct legal advice you receive from your lawyer or other qualified legal professionals.
Get more support and guidance on insurance benefits, medical records and legal forms.
Helpful brings together your insurance benefits, legal documents, and medical records in one personalized place — so you always know what you have, and never have to search again.
Technology for Health Tasks. Mental Health for the Tough Stuff.
Helpful connects your medical records, insurance, and caregiving tasks automatically. And when you need more than logistics, a therapist is here to guide you.
In-Network and Covered
For Individuals, Couples and Families
HIPAA Compliant, Data Stays Private

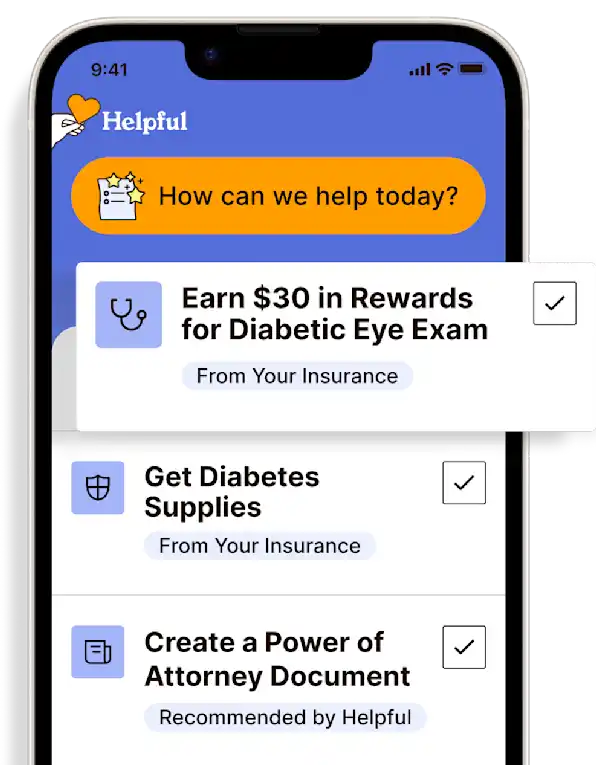
Healthcare Tasks Simplified

From syncing records to spotting drug interactions, Helpful does the heavy lifting, turning complex health info into clear tasks and showing you benefits you can actually use, giving you clarity and control over your care.

In-Network Mental Health

Our licensed therapists are here to support you and your loved ones through stress, burnout, and life’s hardest moments, with an inclusive, compassionate approach that works with most insurance plans.

Create Legal Documents

Plan ahead by creating will, trusts, advance directives and more, that ensure your wishes are honored in the event you can’t speak for yourself -with Helpful guiding you every step of the way.