Definition of Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG)
Coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) is the most common type of heart surgery in the United States, and worldwide.
Get insurance benefits, legal documents, and medical records in one place
Helpful Highlights
Coronary artery bypass surgery is also known as "CABG" (pronounced "cabbage"), "open heart", and "bypass surgery."
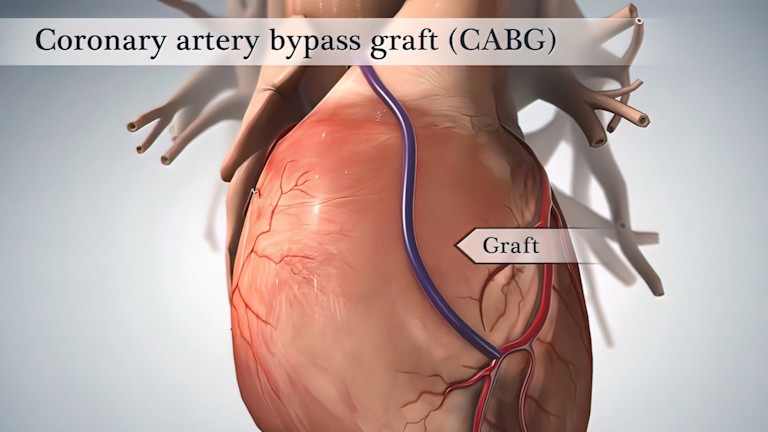
It uses healthy vessels taken from elsewhere in the body to bypass the diseased and blocked vessels of the heart and restore blood flow.
It has proven to lower the risk of a future heart attack, both first and second, as well as the need for additional cardiac procedures.
What is coronary artery bypass graft surgery (CABG)?
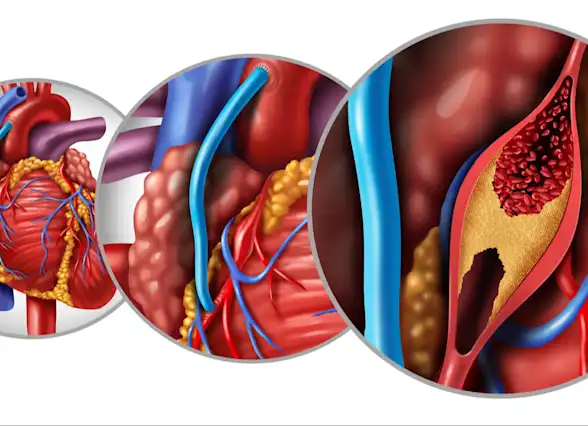
Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) is a surgical procedure to improve blood flow to the heart muscle. It may be needed when the arteries supplying blood to the heart, called coronary arteries, are narrowed or blocked. CABG can reduce symptoms such as chest pain (angina) and shortness of breath, among other symptoms. If left untreated, the blockages can cause a heart attack, or in the case of an existing history of heart attack - another one.
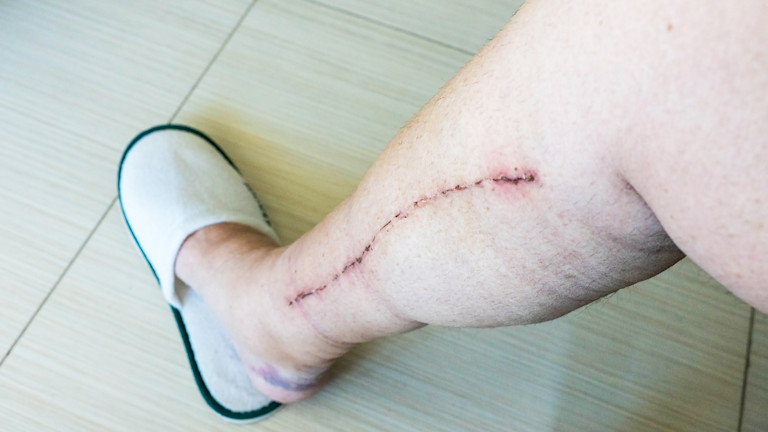
CABG uses healthy blood vessels taken from another part of the body ( called harvesting) and connects them to blood vessels above and below the blocked artery. This creates a new route - or bypass - for blood to flow around the narrowed or blocked section of a coronary artery. The vessels used for bypass are usually taken from the leg, arm, or chest. A single, long vessel from any of these locations may be used to create multiple bypass segments.
Proven procedure
About 200,000 bypass surgeries are performed in the U.S. every year. It is the most common type of heart surgery in the U.S. and worldwide. CABG has proven to lower the risk of future heart attack, both first and second, and the need for additional cardiac procedures. It has also been proven to decrease or eliminate chest pain (called angina), improve survival rates, and lengthen life expectancy.
RESOURCES
American Heart Association (AHA) - Heart Surgery & Recovery Resources
Cleveland Clinic – Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery
Johns Hopkins Medicine – Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Surgery
Mayo Clinic – Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery
No content in this app, regardless of date, should ever be used as a substitute for direct medical advice from your doctor or other qualified clinician.
Get more support and guidance on insurance benefits, medical records and legal forms.
Helpful brings together your insurance benefits, legal documents, and medical records in one personalized place — so you always know what you have, and never have to search again.
Technology for Health Tasks. Mental Health for the Tough Stuff.
Helpful connects your medical records, insurance, and caregiving tasks automatically. And when you need more than logistics, a therapist is here to guide you.
In-Network and Covered
For Individuals, Couples and Families
HIPAA Compliant, Data Stays Private

Healthcare Tasks Simplified

From syncing records to spotting drug interactions, Helpful does the heavy lifting, turning complex health info into clear tasks and showing you benefits you can actually use, giving you clarity and control over your care.

In-Network Mental Health

Our licensed therapists are here to support you and your loved ones through stress, burnout, and life’s hardest moments, with an inclusive, compassionate approach that works with most insurance plans.

Create Legal Documents

Plan ahead by creating will, trusts, advance directives and more, that ensure your wishes are honored in the event you can’t speak for yourself -with Helpful guiding you every step of the way.