Wellcare Dual Liberty (HMO D-SNP) (009): Colorectal Cancer Screening (Colonoscopy and alternatives)
Colorectal cancer screening detects cancer early, increases survival rates, and prevents cancer by finding and removing precancerous polyps
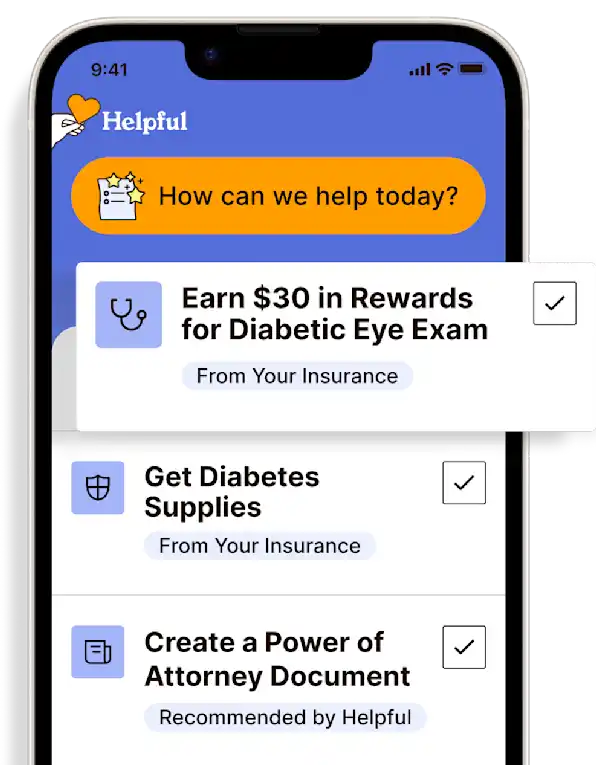
Access all my benefitsGet insurance benefits, legal documents, and medical records in one place
How To Receive
Details on how to apply
There is no coinsurance, copayment, or deductible for a Medicare-covered colorectal cancer screening exam, excluding barium enemas, for which coinsurance applies. If your doctor finds and removes a polyp or other tissue during the colonoscopy or flexible sigmoidoscopy, the screening exam becomes a diagnostic exam and subject to a $0 copay for your doctors’ services.
The following screening tests are covered:
Colonoscopy has no minimum or maximum age limitation and is covered once every 120 months (10 years) for patients not at high risk, or 48 months after a previous flexible sigmoidoscopy for patients who are not at high risk for colorectal cancer, and once every 24 months for high risk patients after a previous screening colonoscopy or barium enema.
Flexible sigmoidoscopy for patients 45 years and older. Once every 120 months for patients not at high risk after the patient received a screening colonoscopy. Once every 48 months for high risk patients from the last flexible sigmoidoscopy or barium enema.
Screening fecal-occult blood tests for patients 45 years and older. Once every 12 months.
Multitarget stool DNA for patients 45 to 85 years of age and not meeting high risk criteria. Once every 3 years.
Blood-based Biomarker Tests for patients 45 to 85 years of age and not meeting high risk criteria. Once every 3 years.
Barium Enema as an alternative to colonoscopy for patients at high risk and 24 months since the last screening barium enema or the last screening colonoscopy.
Barium Enema as an alternative to flexible sigmoidoscopy for patient not at high risk and 45 years or older. Once at least 48 months following the last screening barium enema or screening flexible sigmoidoscopy.
Get more support and guidance on insurance benefits, medical records and legal forms.
Helpful brings together your insurance benefits, legal documents, and medical records in one personalized place — so you always know what you have, and never have to search again.
The overall lifetime risk of developing colorectal cancer is 1 in 23 for men and 1 in 25 for women, and risk increases with age. However, about 90% of colorectal-related deaths are thought to be preventable. Therefore, everyone is encouraged to start regular colorectal cancer screenings at age 50 (the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recently lowered this to age 45, though plan coverage starts at 50). There are three groups of colorectal cancer screens—visual/structural (flexible sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy), fecal-based (FIT, gFOBT, and mt-sDNA), and blood-based biomarkers. While there are some differences between these tests to consider, the most important thing is to get screened, no matter which test is selected.
Colorectal cancer screenings are recommended for people who are at average risk of colorectal cancer, which is essentially everyone between the ages of 45–75 (after age 75, people should speak with their doctor and base screening on preferences, life expectancy, overall health, and prior screening history). People are considered at average risk if they do NOT have a personal history of colorectal cancer or certain types of polyps, a family history of colorectal cancer, a personal history of inflammatory bowel disease (ulcerative colitis [UC] or Crohn’s), a confirmed or suspected hereditary colorectal cancer syndrome such as FAP or Lynch, or a personal history of radiation to the abdomen or pelvic area to treat prior cancer.
Available screenings
Visual/Structural: flexible sigmoidoscopy (or barium enema as an alternative) every 48 months, colonoscopy every 10 years (or every 2 years if high risk), and newer CT colonography.
Fecal-based: highly sensitive fecal immunochemical test (FIT) or highly sensitive guaiac-based fecal occult blood test (gFOBT) every 12 months, and multi-targeted stool DNA test every 36 months.
Blood-based: blood-based biomarker test to screen for colorectal cancer every 3 years if between ages 45-85, show symptoms of colorectal disease (lower gastrointestinal pain, blood in stool, positive FIT or gFOBT), and at average risk for developing colorectal cancer.
The flexible sigmoidoscopy differs from the traditional colonoscopy in that it is a shorter test that only examines the rectum and sigmoid colon versus a thorough look at the whole of the large bowel, up to where it meets the small bowel (as with a colonoscopy). Preparation for both tests is the same.
Technology for Health Tasks. Mental Health for the Tough Stuff.
Helpful connects your medical records, insurance, and caregiving tasks automatically. And when you need more than logistics, a therapist is here to guide you.
In-Network and Covered
For Individuals, Couples and Families
HIPAA Compliant, Data Stays Private

Healthcare Tasks Simplified

From syncing records to spotting drug interactions, Helpful does the heavy lifting, turning complex health info into clear tasks and showing you benefits you can actually use, giving you clarity and control over your care.

In-Network Mental Health

Our licensed therapists are here to support you and your loved ones through stress, burnout, and life’s hardest moments, with an inclusive, compassionate approach that works with most insurance plans.

Create Legal Documents

Plan ahead by creating will, trusts, advance directives and more, that ensure your wishes are honored in the event you can’t speak for yourself -with Helpful guiding you every step of the way.